Author: Sudhendu Pandey
This article is the combined effort of Amulya Nidhi, Venkata Sai Karthik, and various colleagues of mine at kipi.ai!
The post goes over the following sections in detail. But our main agenda is to go through various Data Sharing Patterns enabled by Snowflake.
- What is Data Sharing in Snowflake
- Understanding the Components
- Marketplace Listing
- Data Sharing Decision Tree
- Data Sharing Design Patterns
- Data Sharing Security Considerations
What is Data Sharing in Snowflake
Data Sharing is a Snowflake feature that allows you to share your Snowflake Data with users in other Snowflake accounts.
Why would it make any sense to use Snowflake Data Sharing (SDS) in comparison to, let’s say, sharing data over files, or via exports or providing others access to your database directly?
Few reasons:

Note: Provider is the term for whoever is the owner of the data. The consumer is the party consuming that data. These are standard terms in Snowflake.
Understanding the Components
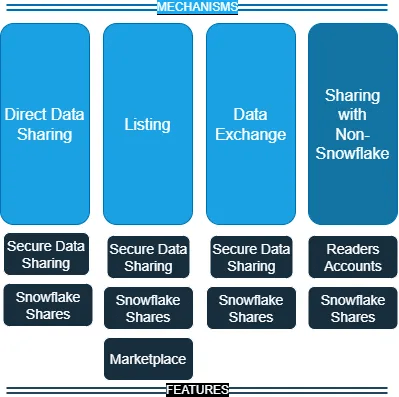
There are five main features of Snowflake Data Sharing:
- Secure Data Sharing
- Snowflake Shares
- Readers Accounts
- Marketplace
- Exchange Hub

The below diagram shows how each of these features enables different types of data sharing within Snowflake. The important thing to notice here is Direct Data Sharing, Data Listing, and Data Exchange are just enhanced versions of Secure Data Sharing.
Also, Readers Account with Snowflake Shares enable Data Sharing with non-Snowflake consumers.
Marketplace Listing
Snowflake Marketplace is a central hub for DaaS (Data As A Service) and now Application As a Service. If your organization creates data that can be shared and/or monetized, Snowflake offers that right from within the platform. What more? This is completely self-service (for both provider and consumers) and the consumers would need to search and then get the data, all in real time.
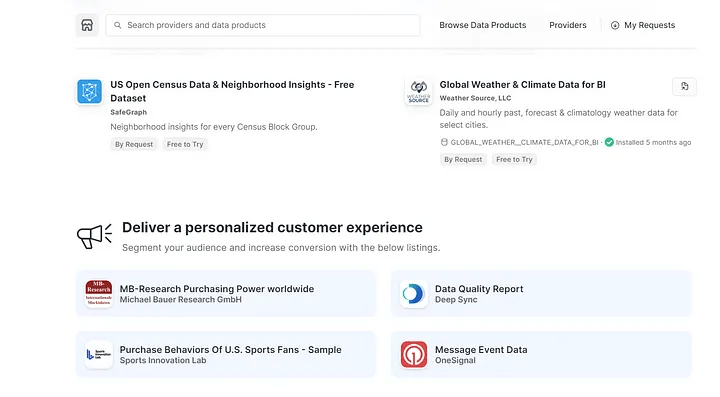
Free Listing: A free listing is available privately or on the Snowflake Marketplace, and provides instant access to a published dataset.
Private Listing: Private listings let you take advantage of the capabilities of listings to share data and other information directly with another Snowflake account in any Snowflake region.
Paid Listing: A paid listing is available privately or on the Snowflake Marketplace. As a provider, you can create paid listings to charge consumers to access or use your listing.
Personalized Listing: A personalized listing lets consumers request specific datasets from providers.
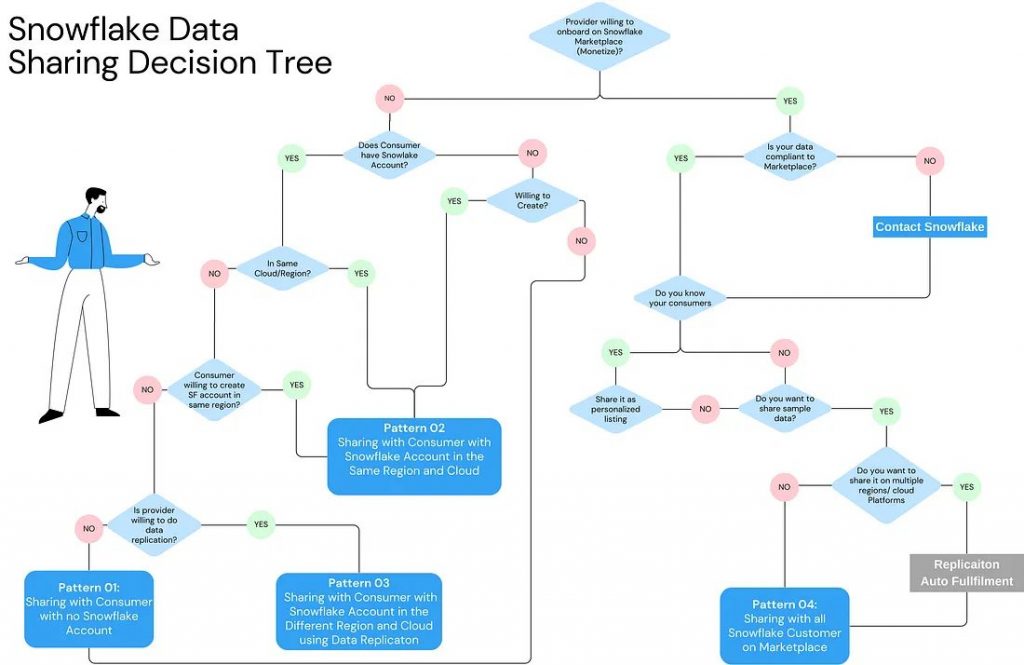
Data Sharing Decision Tree
Itis one thing to know about the concept, but when to use what is useful is the more important part. Have you ever wondered:
Should I use Data Sharing or a reader account?
Why should I do a free listing? What does personalized listing mean?
How should I share data if the consumers are not on Snowflake? Or in a different region?
The below decision tree is an attempt to simply the various Snowflake data-sharing flows and how to decide what suits best for your needs best.
Data Sharing Patterns In Snowflake
Once we understand the flow, the next step is to understand the patterns and various considerations. Below is a high-level guide on various Snowflake Data Sharing Patterns. Each pattern is defined using the following:
- Use-case
- Pattern Details
- Pattern COnsideration
- Implementation Steps
- Cost Considerations
We are going to cover the following four patterns based on our decision tree. Knowing how quickly Snowflake evolves, some of these patterns might bifurcate or consolidate.
- Pattern 01: Sharing with Non-Snowflake Consumers
- Pattern 02: Sharing with Snowflake Consumer in the Same Region and Cloud
- Pattern 03: Sharing with Snowflake Consumers in the Different Regions and Cloud
- Pattern 04: Sharing with Snowflake Consumers on Snowflake Marketplace
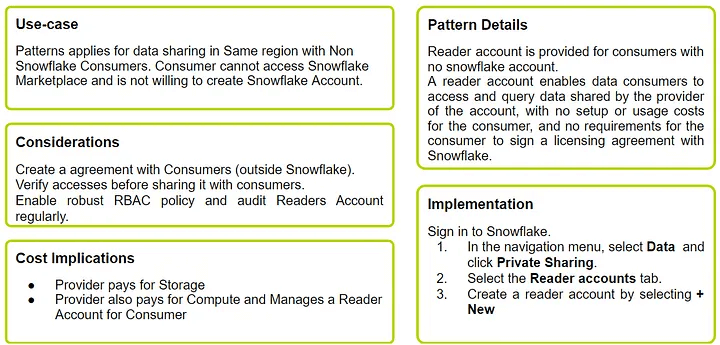
Pattern 01: Sharing with Non-Snowflake Consumers
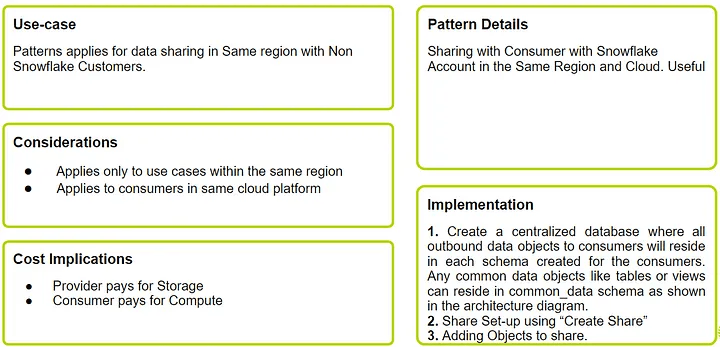
Pattern 02: Sharing with Snowflake Consumer in the Same Region & Cloud
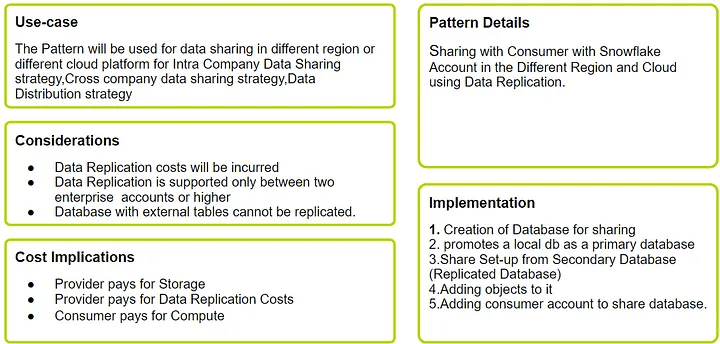
Pattern 03: Sharing with Snowflake Consumers in the Different Regions and Cloud
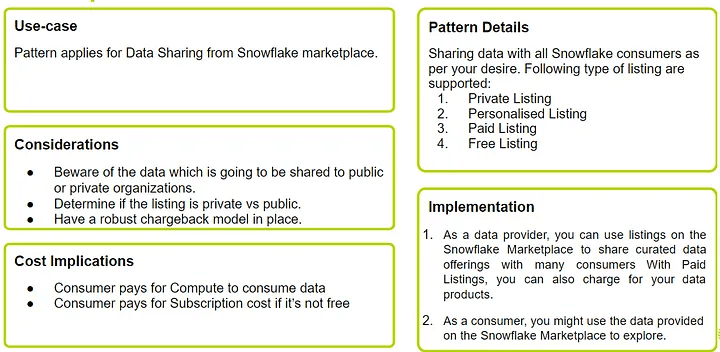
Pattern 04: Sharing with Snowflake Consumers on Snowflake Marketplace
Data Sharing Security Considerations
- Beware of the role and privileges while sharing the reader account
- Any PII/ PHI data sharing is not advisable and should be carefully considered.
- Be careful about who you share data: Only share data with users and organizations that you trust.
- Revoke access to data when it is no longer needed: Revoke access to data when it is no longer needed.
- Monitor your data access: Monitor your data access to identify any unnecessary accesses.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Snowflake uses RBAC to control access to data. This means that you can grant different levels of access to different users and groups.
- Auditing: Snowflake provides auditing capabilities to track access to data. This means that you can see who has accessed your data and other metadata.
- Encryption: Snowflake encrypts data at rest and in transit. This means that your data is protected from unauthorized access even if it is stored on Snowflake’s servers.
Conclusion
Snowflake Data Sharing is a native feature of Snowflake that lets you share and consume data from right within Snowflake. It enables no data movement, governance, and near real-time data availability.